This alarming research article by Randall J. Beck and Jim Harter was published by the Harvard Business Review in 2014. The findings reinforce the urgent need for companies to change the methods by which they identify top managers.
Gallup has found that one of the most important decisions companies make is simply whom they name manager. Yet our analysis suggests that they usually get it wrong. In fact, Gallup finds that companies fail to choose the candidate with the right talent for the job 82% of the time.
Bad managers cost businesses billions of dollars each year, and having too many of them can bring down a company. The only defense against this massive problem is a good offense, because when companies get these decisions wrong, nothing fixes it. Businesses that get it right, however, and hire managers based on talent will thrive and gain a significant competitive advantage.
Managers account for at least 70% of variance in employee engagement scores across business units, Gallup estimates. This variation is in turn responsible for severely low worldwide employee engagement. Gallup reported in two large-scale studies in 2012 that only 30% of U.S. employees are engaged at work, and a staggeringly low 13% worldwide are engaged. Worse, over the past 12 years these low numbers have barely budged, meaning that the vast majority of employees worldwide are failing to develop and contribute at work.
Gallup has studied performance at hundreds of organizations and measured the engagement of 27 million employees and more than 2.5 million work units over the past two decades. No matter the industry, size, or location, we find executives struggling to unlock the mystery of why performance varies so immensely from one workgroup to the next. Performance metrics fluctuate widely and unnecessarily within most companies, in no small part from the lack of consistency in how people are managed. This “noise” frustrates leaders because unpredictability causes great inefficiencies in execution.
Executives can cut through this noise by measuring what matters most. Gallup has discovered links between employee engagement at the business-unit leveland vital performance indicators, including customer metrics; higher profitability, productivity, and quality (fewer defects); lower turnover; less absenteeism and shrinkage (i.e., theft); and fewer safety incidents. When a company raises employee engagement levels consistently across every business unit, everything gets better.
To make this happen, companies should systematically demand that every team within their workforce have a great manager. After all, the root of performance variability lies within human nature itself. Teams are composed of individuals with diverging needs related to morale, motivation, and clarity — all of which lead to varying degrees of performance. Nothing less than great managers can maximize them.
But first, companies have to find those great managers.
If great managers seem scarce, it’s because the talent required to be one is rare. Gallup finds that great managers have the following talents:
- They motivate every single employee to take action and engage them with a compelling mission and vision.
- They have the assertiveness to drive outcomes and the ability to overcome adversity and resistance.
- They create a culture of clear accountability.
- They build relationships that create trust, open dialogue, and full transparency.
- They make decisions that are based on productivity, not politics.
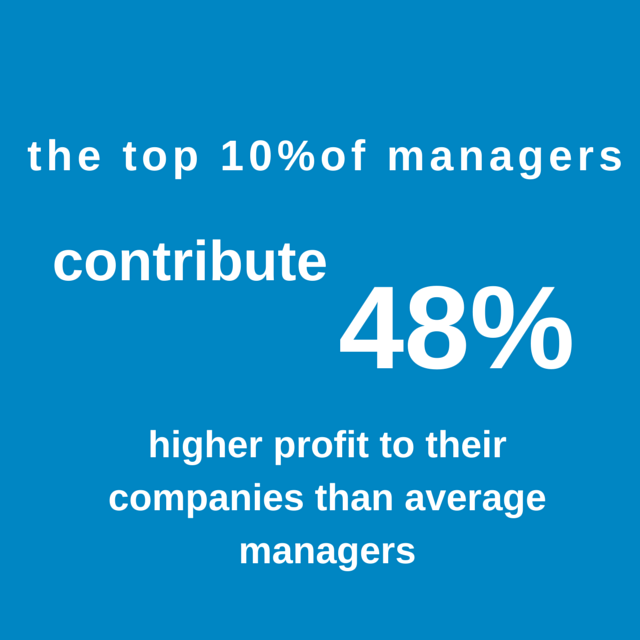
Gallup’s research reveals that about one in ten people possess all these necessary traits. While many people are endowed with some of them, few have the unique combination of talent needed to help a team achieve excellence in a way that significantly improves a company’s performance. These 10%, when put in manager roles, naturally engage team members and customers, retain top performers, and sustain a culture of high productivity. Combined, they contribute about 48% higher profit to their companies than average managers.
It’s important to note that another two in 10 exhibit some characteristics of basic managerial talent and can function at a high level if their company invests in coaching and developmental plans for them.
In studying managerial talent in supervisory roles compared with the general population, we find that organizations have learned ways to slightly improve the odds of finding talented managers. Nearly one in five (18%) of those currently in management roles demonstrate a high level of talent for managing others, while another two in 10 show a basic talent for it. Still, this means that companies miss the mark on high managerial talent in 82% of their hiring decisions, which is an alarming problem for employee engagement and the development of high-performing cultures in the U.S. and worldwide.
Sure, every manager can learn to engage a team somewhat. But without the raw, natural talent to individualize; focus on each person’s needs and strengths; boldly review their team members; rally people around a cause; and execute efficient processes, the day-to-day experience will burn out both the manager and his or her team. As noted earlier, this basic inefficiency in identifying talent costs companies hundreds of billions of dollars annually.
These reasons don’t take into account whether the candidate has the right talent to thrive in the role. Being a very successful programmer, salesperson, or engineer, for example, is no guarantee that someone will be even remotely adept at managing others.
Most companies promote workers into managerial positions because they seemingly deserve it, rather than because they have the talent for it. This practice doesn’t work. Experience and skills are important, but people’s talents — the naturally recurring patterns in the ways they think, feel, and behave — predict where they’ll perform at their best. Talents are innate and are the building blocks of great performance. Knowledge, experience, and skills develop our talents, but unless we possess the right innate talents for our job, no amount of training or experience will matter.
Very few people are able to pull off all five of the requirements of good management. Most managers end up with team members who are at best indifferent toward their work — or are at worst hell-bent on spreading their negativity to colleagues and customers. However, when companies can increase their number of talented managers and double the rate of engaged employees, they achieve, on average, 147% higher earnings per share than their competition.
It’s important to note — especially in the current economic climate — that finding great managers doesn’t depend on market conditions or the current labor force. Large companies have approximately one manager for every 10 employees, and Gallup finds that one in 10 people possess the inherent talent to manage. When you do the math, it’s likely that someone on each team has the talent to lead. But given our findings, chances are that it’s not the manager. More likely, it’s an employee with high managerial potential waiting to be discovered.
The good news is that sufficient management talent exists in every company – it’s often hiding in plain sight. Leaders should maximize this potential by choosing the right person for the next management role using predictive analytics to guide their identification of talent.
For too long, companies have wasted time, energy, and resources hiring the wrong managers and then attempting to train them to be who they’re not. Nothing fixes the wrong pick.